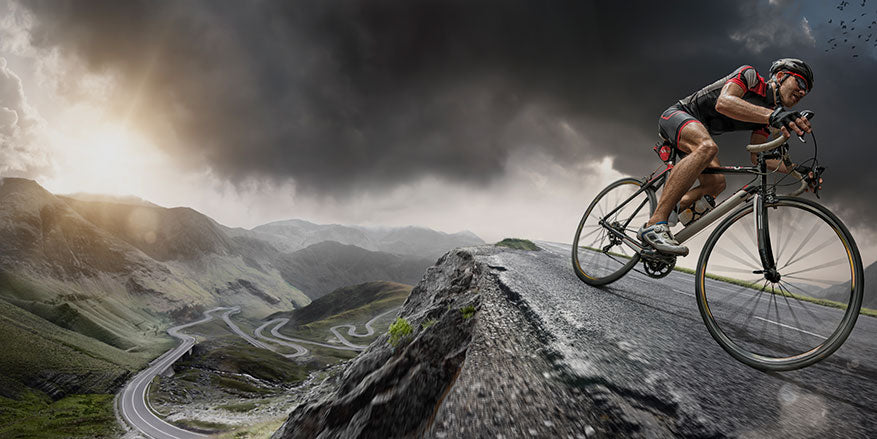
You don't have to stand on one leg while brushing your teeth in the morning or do squats by an open window in the freezing cold—very few people are good at those things. Extreme recommendations are of little help. As a general rule, physical fitness should be achieved simply through everyday activities, like running upstairs or cycling, and optimized through moderate, targeted training.
Of course, this won't be achieved by sitting on the couch for hours. This is where nutrition comes into play. A vegetable- and fruit-based diet with few, but the right fats, as well as the conscious enjoyment of meat and sausage, are just as important as regular fish consumption. Those who pay attention to physical fitness will not only quickly give up smoking but also be cautious about alcohol and sugar, as well as unhealthy additives in their food. You don't have to give up anything, but you will voluntarily pay more attention to what your body needs for its physical fitness. Stay away from fancy diets, but don't eat when you don't feel like it.

Physical fitness is one of the most important aspects of your health
Being physically fit has many benefits:
- The body is approaching its ideal weight. The ideal weight and BMI values are often controversial among experts, and doctors do observe advantages for people who are not entirely slim, for example, with regard to heart disease. However, obesity is known to lead to many other health problems. These include metabolic diseases such as diabetes and joint problems.
- The muscle gains also increase calorie burn, even during rest. This means that, while maintaining the same food intake, you'll automatically lose weight and can still indulge in a piece of cake with a clear conscience. Your figure will also tone up.
- Your circulation stays active, and the performance of your entire body is boosted. This is also noticeable in your private life and at work.
- Physical fitness promotes concentration and lifts mood. Depression is significantly less common in active people. The immune system is also highly active, making the body more resistant to attacks from bacteria and viruses.
- An important benefit for all older people: Good physical fitness prevents falls because it improves your sense of balance and significantly increases your control over your body. Joints are lubricated, muscles strengthened, and the dreaded development of osteoporosis is staved off. Exercise also encourages you to drink more, which is especially important for the proper functioning of all organs in old age. Circulation improves significantly, and your skin looks younger.
To achieve physical fitness , you don't have to get marathon-ready in four weeks. Some experts have concluded that more than half an hour per day, or a maximum of four to five hours per week, is unnecessary and may even be harmful. This certainly depends on many factors: Have you been active before? Did you perhaps even participate in competitive sports? In that case, you certainly need a different program than someone who has never exercised before.
There's also debate about whether personal physical fitness isn't actually achieved differently for each person. One person might exercise little and stay healthy, while another might jog or swim every day and get sick. However, good advice is: take a brisk walk for at least half an hour a day. Your body will tell you what additional cycling or team sports you should incorporate for your individual physical fitness, if you listen carefully.

Sport not only makes you fit, but also smart
More and more studies are proving that exercise increases mental performance. In addition to short-term effects, more and more long-term, profound effects are being discovered. Researchers are even going so far as to say that exercise can actually make the brain bigger.
What happens in the brain when we move?
When you exercise, you're not just training your body, but also your brain. Through exercise, we not only keep our muscles fit, strengthen bones, or improve circulation – when we exercise, both short-term and long-term changes occur in the brain. The short-term effects, such as increased blood flow and nutrient supply, and lowered stress hormone levels, are well known. The truly profound effects, which even change brain structure and only occur with regular exercise over a longer period, are far less well known.
Short-term effects - A reset for the stressed brain
In the short term, exercise helps reduce your stress levels and eliminate negative thoughts. When we exercise, blood flow increases, and the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine, known as the happiness hormones, are released. These help reduce stress, calm anxiety, and increase well-being. Problems often seem easier to solve after exercise, and you come up with new approaches. The reset also occurs because resources are used during exercise, primarily in the motor cortex, the region of the brain primarily responsible for muscles, breathing, and body awareness. Since only a limited number of resources are available, they are consequently diverted from frontal areas. The more intensively we exercise, the more resources and energy the motor cortex consumes—so it's worth really pushing yourself during exercise. This leads to the cognitive processes of the prefrontal cortex being shut down. You can't physically exert yourself and think intensely at the same time—you simply function. This state is very similar to the flow state known from motivational research. Therefore, many athletes report that they can clear their heads and concentrate better after exercising.
Long-term effects – growth through movement
In addition to the positive short-term effects, exercise also has extremely positive long-term, structural effects on our brain. Through exercise or physical activity and the associated increased cerebral blood flow, increased amounts of nerve growth substances, so-called neurotropins, are produced. These support the continuous formation of new neurons in the brain. Studies have shown that athletes have significantly more brain mass than non-athletes, especially in the so-called supplementary motor area. However, scientists have also found greater brain mass in other brain regions not responsible for physical activity. The hippocampus, which plays a key role in emotional processing, is also more developed in athletes. This change is promoted by the improved supply of growth substances, but also by other effects. Regular exercise has a lasting impact on our hormone balance because it leads to a slower breakdown of the neurotransmitter dopamine. As described above, dopamine is not only a natural mood enhancer, it is also needed for important cognitive processes in the prefrontal cortex. When dopamine levels drop, attention, concentration, and other mental abilities decline. In people who are not physically active, dopamine levels actually decline continuously over the course of life. Thus, through physical activity, you can increase your dopamine levels in the short term and slow the process of steady decline in the long term. Furthermore, through exercise, especially running, you can improve your spatial awareness and concentration skills.

Which sports are most suitable?
The best news from the studies is that it's not the sport itself that matters, but rather regular exercise in general. Endurance sports like jogging, interval training, or rowing are particularly suitable. The important thing is that you enjoy your sport and reach an intensity that optimally challenges you, because only then can you best reap the benefits described above. The right attitude is also crucial. Especially if you're under a lot of stress, you shouldn't view exercise as wasted time, but rather as a conscious way to switch off, through which you gather energy for upcoming challenges. Of course, there are many other ways to switch off – but the best way to keep your body and mind fit at the same time is through exercise! If you really want to get started now, we recommend our article, which will teach you how to best achieve your goals!
Regular physical activity promotes fitness, strengthens muscles and endurance, and promotes a healthy body image. Physical activity also promotes the formation of new synapses and the strengthening of existing brain connections. Studies have shown that people can concentrate better after exercise. Therefore, those who exercise not only train their bodies but also their brains.
Strolling - Walking - Jogging - Cycling
Running in the fresh air supplies our brain with oxygen, releases endorphins, and reduces stress. Just walking can increase blood flow to the brain by about 20%. The increased blood flow improves the transport of not only oxygen but also biochemicals. Especially when jogging, however, you should make sure to run within your optimal personal heart rate limits. You've reached your optimal running pace when you can easily hold a conversation while jogging.
To swim
Front crawl swimming, in particular, has positive effects on our brains. The cross-over movements involved in front crawl swimming strengthen the connection between the right and left hemispheres of the brain, thus improving coordination and cognition.
Juggle
While less physically demanding, juggling primarily challenges the brain. The collaboration of both hemispheres of the brain trains concentration, perception, and attention.
Golf
Golf isn't the greatest physical challenge, but it does increase concentration because it challenges our brains in a unique way. Golfers memorize the entire course beforehand, which is the perfect mental workout for our brains.
yoga
Scientists have discovered that just 20 minutes of yoga a day is enough to significantly improve our memory performance. Yoga has been proven to strengthen our cognitive abilities, improving our reaction times and precision.
Climb
Climbing and bouldering are good for both physical and mental fitness. Climbing strengthens working memory and improves coordination and body awareness.
Ideal training times
It's best to use the late afternoon or early evening to exercise. Most people are at their best between 4 and 7 p.m. Starting around 9 p.m., the cardiovascular system slows down, and performance declines. The body prepares for sleep. Therefore, those who exercise after 9 p.m. often struggle with falling asleep. If you still want to exercise later in the day, you should choose sports like yoga, Pilates, or Tai Chi, which allow the body to relax while still exercising.
BRAINEFFECT ROCKET C8 - the ultimate power shot for sports
If you want to naturally support your physical and cognitive abilities during exercise, BRAINEFFECT ROCKET C8 is the ideal solution. BRAINEFFECT ROCKET C8 is an MCT oil made from 100% caprylic acid, which helps produce ketone bodies during a ketogenic or low-carb diet. You can read more about the effects of MCT oil here, and you can buy the product here.
Sources:
Schneider, S (2013), “Physical Activity and Mental Health”; in Proceedings of the 5th World Health Summit.Schlaffke L, Lissek S, Lenz M, Brüne M, Juckel G, Hinrichs T, Platen P, Tegenthoff M, Schmidt-Wilcke T, (2014), Sports and brain morphology - A voxel-based morphometry study with endurance athletes and martial artists. Neuroscience. 259:35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.11.046.
{{widget type="egproducts/list_featured" template="elegento/products/listslider.phtml"}}