Strength training, endurance training, mental stimulation – to train your body and mind, you need energy. Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP for short, is the body's natural booster that helps you achieve your desired peak performance. Learn how to replenish your energy reserves here.
Table of contents
1. Adenosine triphosphate – What is it?
Adenosine triphosphate , abbreviated ATP , is the main energy storage of cells . It consists of a bond of adenosine and three phosphate groups. Every single cell in the human body derives its energy from ATP .
If no ATP is present , the cell dies . However, it also works the other way around: If a lot of ATP is present , the cell is particularly active .
This is why it's naturally of great interest to biohackers to increase adenosine triphosphate production . Because more ATP leads to more energy for the body and brain —and who doesn't want that?
BRAINEFFECT HACK : Do you often lie awake in bed late at night and can't fall asleep? Our SLEEP Capsules and SLEEP SPRAY can help you fall asleep faster in the evening thanks to the melatonin they contain.
2. The function of adenosine triphosphate
Muscles, in particular , which are abundant in the human body and not only make you mobile but also functional in the first place, require ATP for propulsion . Metabolism, cell renewal, digestion, concentration – none of this would be possible without ATP.
Without ATP, you couldn't walk, think, or breathe; you simply wouldn't be able to survive. To ensure the battery never runs out, cells constantly produce new ATP.
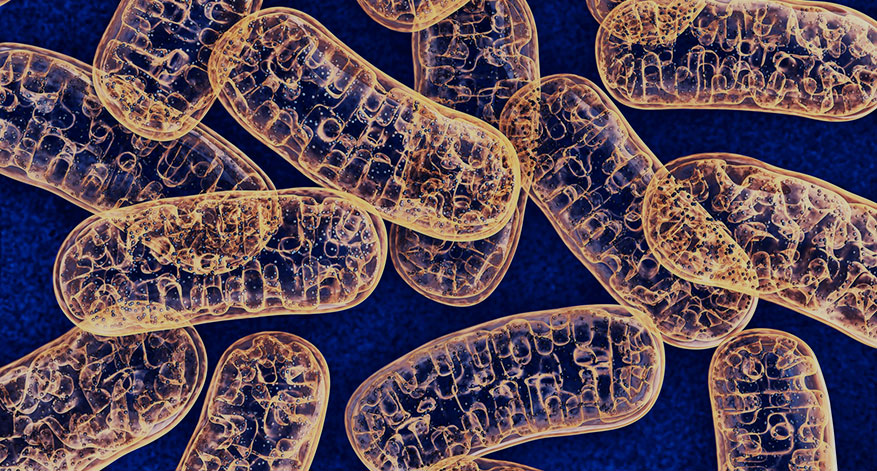
Here's how: During cellular respiration , glucose , oxygen , and water are broken down into water and carbon dioxide in the mitochondria , the cell's mini-powerhouses. This breakdown produces energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate .
Enzymes in the mitochondria break down this ATP into adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and free phosphate. The released energy is dissipated as heat but is primarily used for muscle function.
However, the ADP must then be converted back into ATP. This creates a perpetual cycle that only functions properly with an optimal supply of nutrients.
The body has a sophisticated system for this: energy metabolism. The energy you consume through food —from carbohydrates , proteins , and fats —is stored within ATP molecules until it is needed by the cells.
However, cells don't store their ATP as a permanent energy reserve . After about five seconds of exertion, the ATP is completely used up . Therefore , they need to produce more quickly .
Unfortunately , you can't increase your ATP supply long-term , because ATP can't be stored in advance . However , you can always provide your body with sufficient nutrients for ATP production.
Take-Home Message #1: Without ATP, you cannot survive and perform physically or mentally. However, ATP cannot be stored and must be constantly produced.
BRAINEFFECT HACK : In addition to glucose from carbohydrates and proteins, your body can also use fats in the form of ketone bodies as an energy source. Once you've accustomed your body to fat metabolism, known as ketosis, energy production from fats is even more efficient than from glucose.
For those already in ketosis or who want to help their body produce ketone bodies faster, MCT oil is a perfect option. High-quality MCT oil made from 100% caprylic acid C8, like our ROCKET C8 , provides you with fast ketogenic energy.
3. 3 ways to produce ATP
Adenosine triphosphate must always be available through metabolism, as muscle contractions are often spontaneous—for example, in our ancestors, when hunting or fleeing. The body therefore has three ways to quickly produce ATP:
- Creatine phosphate , which is found in muscle cells , allows ADP to be quickly converted into ATP . The more creatine phosphate there is in the cells, the faster ATP is produced when needed.
However, this anaerobic energy recovery technique works better for short sprints than long marathons. For efforts lasting longer than 10 seconds, Plan B comes into play. - For exertion lasting only a few minutes , glycolysis kicks in : carbohydrates are broken down in muscle cells. The breakdown of glucose molecules produces two ATP molecules per molecule.
- For endurance training lasting longer than 2 minutes , glycolysis switches to aerobic energy production , which only works effectively with oxygen.
In the mitochondria, during cellular respiration, oxygen splits off energy-rich hydrogen molecules from carbohydrates, proteins and fats, which in turn cause phosphates to bind to ADP and become ATP.
The more ATP produced during aerobic exercise, the more oxygen the cells require. During the respiratory chain, up to 32 ATP molecules are produced per glucose molecule , which is why endurance training is considered very effective for increasing energy .
4. How important is nutrition for ATP production?
Simple answer: very important ! Because without fuel, no fire can start. The more valuable nutrients your body receives, the better it can convert them into energy. For energy metabolism, for example, it particularly needs calcium , magnesium, and phosphorus, as well as sufficient vitamin D , so that the nutrients can be metabolized effectively.
Since ATP isn't stored as an energy reserve in the cells, regular meals are necessary for optimal performance . The body converts carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into ATP, which, however, is only available in the cells for a short time and is completely consumed within a few seconds during muscle movement. Therefore, replenishment is urgently needed to keep energy metabolism running.
BRAINEFFECT HACK : Make sure you eat high-quality foods like long-chain carbohydrates, which provide you with energy for longer than unhealthy sweets, which usually only provide energy for a very short period of time.
Likewise, when it comes to fats, you can make sure to use fats and oils from which your body can generate energy most effectively. For example, MCT oil with the highest possible content of caprylic acid C8.
In our shop, you can get ROCKET C8 MCT oil, which consists of 100% caprylic acid and is therefore particularly easily converted into ketones by your body.

5. ATP for muscle building
Adenosine triphosphate provides muscles with the energy they need to contract . The more energy available, the better the muscle functions and the more powerful it is. If little energy is available, every movement becomes strenuous.
Anyone who wants to achieve success in their training should ensure that their muscles are optimally supplied with nutrients . Only when they have sufficient energy can they deliver the desired performance.
For targeted muscle building, you need more ATP. This allows you to push yourself to your limits more effectively during training sessions .
But don't forget in your ambition: Muscles only build up during the recovery phase after training, and then only if you provide them with sufficient protein.
The energy stores also need to be replenished again and again and require a regeneration break between performance peaks.
Take-Home Message #2: To have more energy, the body needs sufficient nutrients for ATP production. There are various production pathways to ensure that sufficient ATP is always present in the cells.
BRAINEFFECT HACK : Sleep is essential for your recovery and muscle building. Our SLEEP capsules and handy SLEEP SPRAY provide you with melatonin and can help you fall asleep faster.
6. The Biohack: More mitochondria – more energy
Since it's not possible to replenish the cells' ATP stores , you have to target another source to increase your mental and physical performance: the mitochondria . Every cell consists of thousands of these tiny powerhouses, which can multiply or degrade – depending on the body's energy needs.
So, if you're generally sluggish and like to lounge around on the couch, your mitochondria count will decrease. However, if you're active and constantly challenge your body and mind, your mitochondria count will increase.
Therefore, the principle is quite simple: Increase your energy needs ! Here are some effective tips that you can easily incorporate into your daily routine:
-
Cold thermogenesis : Cold is good for you, so grit your teeth and start with a cold shower or ice bath. To compensate for the cold , your body needs to produce more heat —and therefore more energy.
Oxidation occurs in brown adipose tissue , which, unlike white adipose tissue, has a particularly high concentration of mitochondria . With regular cold application , you'll soon notice your energy levels rising.
-
Endurance training : Running, cycling, swimming—you can train whatever you want, as long as it's endurance-based. This increases the number of mitochondria in muscle fibers , as a study from Toronto shows [1].
Incidentally, the training effect is independent of age and even occurs in seniors through regular exercise. A side note: At the same time, endurance training also produces more mitochondria in the brain , brain researchers from South Carolina discovered [2]. Regular exercise is therefore a true win-win situation!
-
Ketogenic diet : This diet reduces carbohydrate intake to such an extent that the body draws its energy from fat reserves. Energy from fats such as MCT oils (e.g., ROCKET C8 ) is particularly valuable .
For example, Kristopher Bough found that after just 1 to 3 weeks of a ketogenic diet, the density of mitochondria in the hippocampus increased by 46 percent [3].
-
Intermittent fasting : Intermittent fasting has enjoyed growing popularity for years – and rightly so!
In addition to a variety of positive effects on the aging process and weight reduction, this fasting according to the 16/8 rule can do one thing above all: increase your energy level and thus your performance .
You eat normally during the eight hours and fast for the remaining 16 hours. Alternatively, you can fast one or two days per week and eat normally otherwise.
Intermittent fasting promotes ketosis and can stimulate mitochondrial production, according to a study from Harvard University [4].
Take-Home Message #3: To boost your energy levels, you can increase your mitochondria count, for example through cold exposure, endurance training, and diet.
7. Conclusion
ATP is your cells' main energy storage. For your cells to function optimally, they must always be supplied with sufficient ATP. This only works if you supply them with high-quality carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
You can't increase your ATP stores yourself to improve your energy production. But you can ensure that your body produces more mitochondria, which in turn contain ATP.
8. Sources
[1] https://link.springer.com/article/10.2165/00007256-200333110-00001
[2] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21817111
[3] https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01846.x
[4] https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(17)30612-5
{{widget type="egproducts/list_featured" template="elegento/products/listslider.phtml"}}